Me Myself and I
Tuesday, November 23, 2010
Moving to new location
I've beeen doing some research and i decided to make a maze game when ever the red square is touched it moves to a new location on the map and when you touch it three times there is a new level. When the main sprite touches the red box it moves to a new location in the maze. After it is cought for the third time it goes to the next level
Tuesday, November 9, 2010
glide
Today i learned how to make my sprite glide any direction i want it to. I lerned that the lesser the seconds the faster it glide and the more the seconds the slower in glide. It glides staight until it hits the coordinant u types in.
Wednesday, October 27, 2010
Scratch controlls
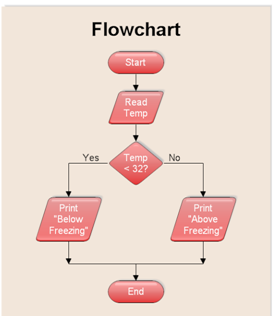
Wednesday, October 20, 2010
simple flowcharts
Tuesday, October 12, 2010
Computer algorithms
1. Algorithms
an algorithm is any set of detailed instructions which results in a predictable end-state from a known beginning. Algorithms are only as good as the instructions given, however, and the result will be incorrect if the algorithm is not properly defined.
2. Pseudocode
An outline of a program, written in a form that can easily be converted into real programming statements. For example, the pseudocode for a bubble sort routine might be written:
while not at end of list
compare adjacent elements
if second is greater than first
switch them
get next two elements
if elements were switched
repeat for entire list
Pseudocode cannot be compiled nor executed, and there are no real formatting or syntax rules. It is simply one step - an important one - in producing the final code. The benefit of pseudocode is that it enables the programmer to concentrate on the algorithms without worrying about all the syntactic details of a particular programming language. In fact, you can write pseudocode without even knowing
3. Machine Language
The lowest-level programming language (except for computers that utilize programmable microcode) Machine languages are the only languages understood by computers. While easily understood by computers, machine languages are almost impossible for humans to use because they consist entirely of numbers. Programmers, therefore, use either a high-level programming language or an assembly language. An assembly language contains the same instructions as a machine language, but the instructions and variables have names instead of being just numbers.
4. High Level Computer Language
Programs written in high-level languages are translated into assembly language or machine language by a compiler. Assembly language programs are translated into machine language by a program called an assembler.
Every CPU has its own unique machine language. Programs must be rewritten or recompiled, therefore, to run on different types of computers.
5. Flowchart
a diagram of the sequence of operations in a computer program or an accounting system
6. Sequence
The typical features of a telephone call are as follows: It begins an opening section featuring a hello or identification of the answering party. This is followed by a hello and identification of the calling party, with an exchange of how are you. Then the first topic is announced, followed by topic closing and shifts to (preferably) related topics. This is followed by a closing section consisting of elements like passing turns of okay, an identification of the type of call [Well, I just wanted to call and …], more passing turns, and an exchange of good-byes.
7. Selection
A carefully chosen or representative collection of people or things
8. Repetition
the act of repeating; repeated action, performance, production, or presentation.
1. Opening a door and entering a room.
an algorithm is any set of detailed instructions which results in a predictable end-state from a known beginning. Algorithms are only as good as the instructions given, however, and the result will be incorrect if the algorithm is not properly defined.
2. Pseudocode
An outline of a program, written in a form that can easily be converted into real programming statements. For example, the pseudocode for a bubble sort routine might be written:
while not at end of list
compare adjacent elements
if second is greater than first
switch them
get next two elements
if elements were switched
repeat for entire list
Pseudocode cannot be compiled nor executed, and there are no real formatting or syntax rules. It is simply one step - an important one - in producing the final code. The benefit of pseudocode is that it enables the programmer to concentrate on the algorithms without worrying about all the syntactic details of a particular programming language. In fact, you can write pseudocode without even knowing
3. Machine Language
The lowest-level programming language (except for computers that utilize programmable microcode) Machine languages are the only languages understood by computers. While easily understood by computers, machine languages are almost impossible for humans to use because they consist entirely of numbers. Programmers, therefore, use either a high-level programming language or an assembly language. An assembly language contains the same instructions as a machine language, but the instructions and variables have names instead of being just numbers.
4. High Level Computer Language
Programs written in high-level languages are translated into assembly language or machine language by a compiler. Assembly language programs are translated into machine language by a program called an assembler.
Every CPU has its own unique machine language. Programs must be rewritten or recompiled, therefore, to run on different types of computers.
5. Flowchart
a diagram of the sequence of operations in a computer program or an accounting system
6. Sequence
The typical features of a telephone call are as follows: It begins an opening section featuring a hello or identification of the answering party. This is followed by a hello and identification of the calling party, with an exchange of how are you. Then the first topic is announced, followed by topic closing and shifts to (preferably) related topics. This is followed by a closing section consisting of elements like passing turns of okay, an identification of the type of call [Well, I just wanted to call and …], more passing turns, and an exchange of good-byes.
7. Selection
A carefully chosen or representative collection of people or things
8. Repetition
the act of repeating; repeated action, performance, production, or presentation.
1. Opening a door and entering a room.
- walk straight toward the door
- stop half a mitre from the door
- reach hand out then grab the door knob
- Turn clockwise then push
- walk and push door at the same time
- if door fully then open enter room
- Approach traffic light
- Check color of light
- If the light is green then continue
- If the light is red then stop
- If the light is orange then slow down
Tuesday, September 21, 2010
Broadband Research
1. What is broadband?
2. Outline the methods of delivery of broadband (wireless, cable, ADSL and fibre)? Identify the speed of each method.
3. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
4. Give examples of broadband providers and identify the costs.
5. The Federal Government is thinking of rolling out a national broadband network (The NBN). Research the NBN and find out:
a. what method of delivery it will use
b. the expected speed
c. the expected costs
6. Do you think Australians should invest in The NBN? Justify your answer.
2. Outline the methods of delivery of broadband (wireless, cable, ADSL and fibre)? Identify the speed of each method.
3. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
4. Give examples of broadband providers and identify the costs.
5. The Federal Government is thinking of rolling out a national broadband network (The NBN). Research the NBN and find out:
a. what method of delivery it will use
b. the expected speed
c. the expected costs
6. Do you think Australians should invest in The NBN? Justify your answer.
Tuesday, August 31, 2010
bibliography and my multimedia site
Wireless broadband
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-wireless-broadband.htm http://news.cnet.com/2100-1039_3-6178977.html http://top10.com/broadband/guides/what_is_a_wireless_router/
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OG9i2VPY_LE&feature=related
Social Networking
http://www.whatissocialnetworking.com/
http://communication.howstuffworks.com/how-social-networks-work.htm http://www.linkedin.com/answers/technology/web-development/TCH_WDD/536683-51986603 http://www.mcafee.com/us/local_content/misc/threat_center/msj_future_social_networking.pdf http://communication.howstuffworks.com/how-social-networks-work4.htm
Handheld Devices
http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/handheld http://uis.georgetown.edu/handhelds/handhelds.types.html http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/travel/pda6.htm http://www.gizmag.com/go/5187/
CPU
http://www.howstuffworks.com/pc.htm
http://video.about.com/pcsupport/installCPU-mov.htm http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/247866-28-future http://www.ehow.com/about_4587172_different-types-processors.html http://www.ehow.com/list_6669743_disadvantages-intel-processor.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sandy_Bridge_(microarchitecture)
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-different-types-of-beaded-necklaces.htm
My site URL
www.wix.com/08tmuza/multimedia_-wixcom
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-wireless-broadband.htm http://news.cnet.com/2100-1039_3-6178977.html http://top10.com/broadband/guides/what_is_a_wireless_router/
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OG9i2VPY_LE&feature=related
Social Networking
http://www.whatissocialnetworking.com/
http://communication.howstuffworks.com/how-social-networks-work.htm http://www.linkedin.com/answers/technology/web-development/TCH_WDD/536683-51986603 http://www.mcafee.com/us/local_content/misc/threat_center/msj_future_social_networking.pdf http://communication.howstuffworks.com/how-social-networks-work4.htm
Handheld Devices
http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/handheld http://uis.georgetown.edu/handhelds/handhelds.types.html http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/travel/pda6.htm http://www.gizmag.com/go/5187/
CPU
http://www.howstuffworks.com/pc.htm
http://video.about.com/pcsupport/installCPU-mov.htm http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/247866-28-future http://www.ehow.com/about_4587172_different-types-processors.html http://www.ehow.com/list_6669743_disadvantages-intel-processor.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sandy_Bridge_(microarchitecture)
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-different-types-of-beaded-necklaces.htm
My site URL
www.wix.com/08tmuza/multimedia_-wixcom
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)